
In 2025, my LinkedIn feed became flooded with SEO thought leaders scrambling to define and stake their claim on the future of consumer search: generative engine optimization (GEO).
Yet, most industry experts face a stark reality – few truly understand how to influence brand visibility in AI-driven search platforms and large language models (LLMs), let alone explain what this shift means for search marketing or how brands can capitalize on it.
This article unpacks the rise of GEO, debunks common myths, and outlines what businesses must do to adapt before they fall behind.
AI search and LLMs: A new era of information discovery
AI-driven search platforms, like Google’s AI Overviews and Microsoft Bing’s AI-powered results, are redefining how users find information, moving from traditional keyword-based ranking to dynamic, AI-generated answers.
Meanwhile, LLMs, such as ChatGPT and Gemini, power these systems by synthesizing vast amounts of data to provide conversational, non-deterministic responses.
Ultimately, brands that adapt to how AI retrieves, interprets, and generates information could increase their long-term visibility, while those that don’t risk losing a critical new traffic source.
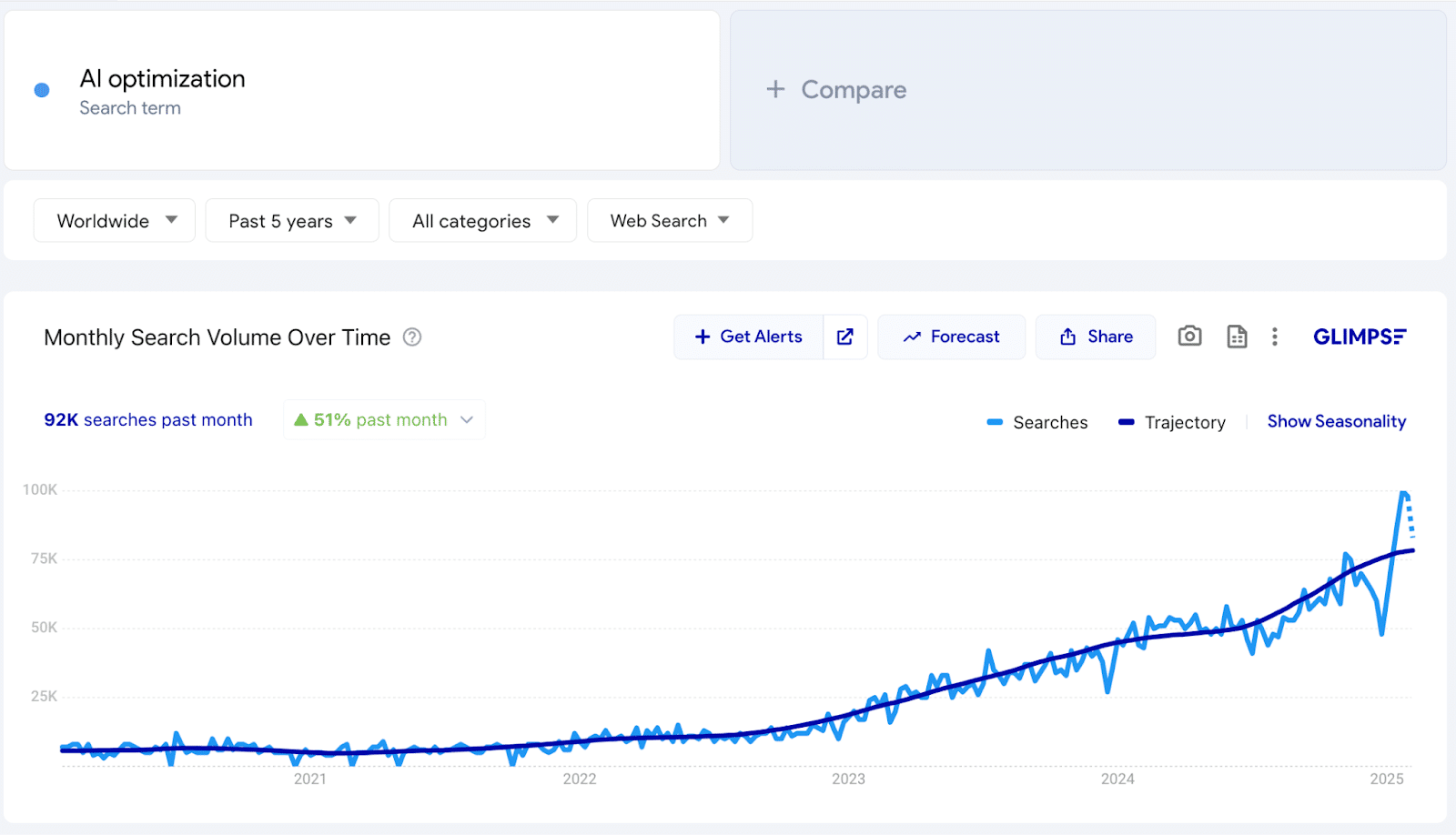
To better understand how these changes are impacting users, I set out to explore the growing friction in organic search and the misconceptions surrounding GEO.
Increasing user friction threatens the value of SERPs for consumers
In October, Fractl (disclosure: I co-founded the agency) studied AI adoption in consumer search. We found that nearly half (48%) of respondents had used ChatGPT or a similar tool within the past week.
As of January, ChatGPT is the 8th most visited website in the world, attracting 4.79 billion visits per month.
Anyone who isn’t studying how to drive brand visibility in AI platforms is already too far behind to be spearheading your marketing efforts and hedging your brand’s future traffic sources.
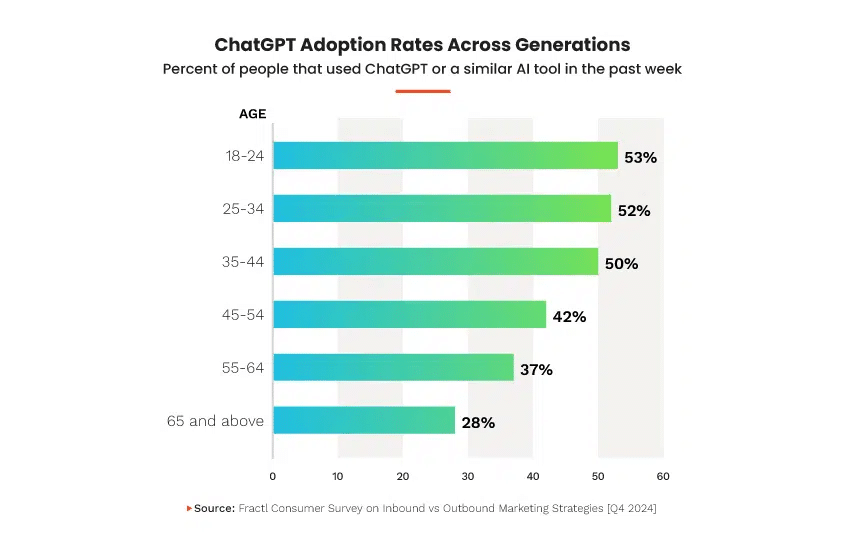
A few weeks ago, when nearly every Google query forced me to complete a tedious CAPTCHA, I felt like I was witnessing the beginning stages of Google Search’s slow collapse.
Surely, a novice searcher would be even more frustrated than me by the growing friction and declining SERP quality, which would further accelerate the shift to newer, more valuable search platforms.
I ran off to our own survey platform to run a quick pulse survey of 1,000 Americans, seeking to understand “What frustrates users most about Google’s search experience?”
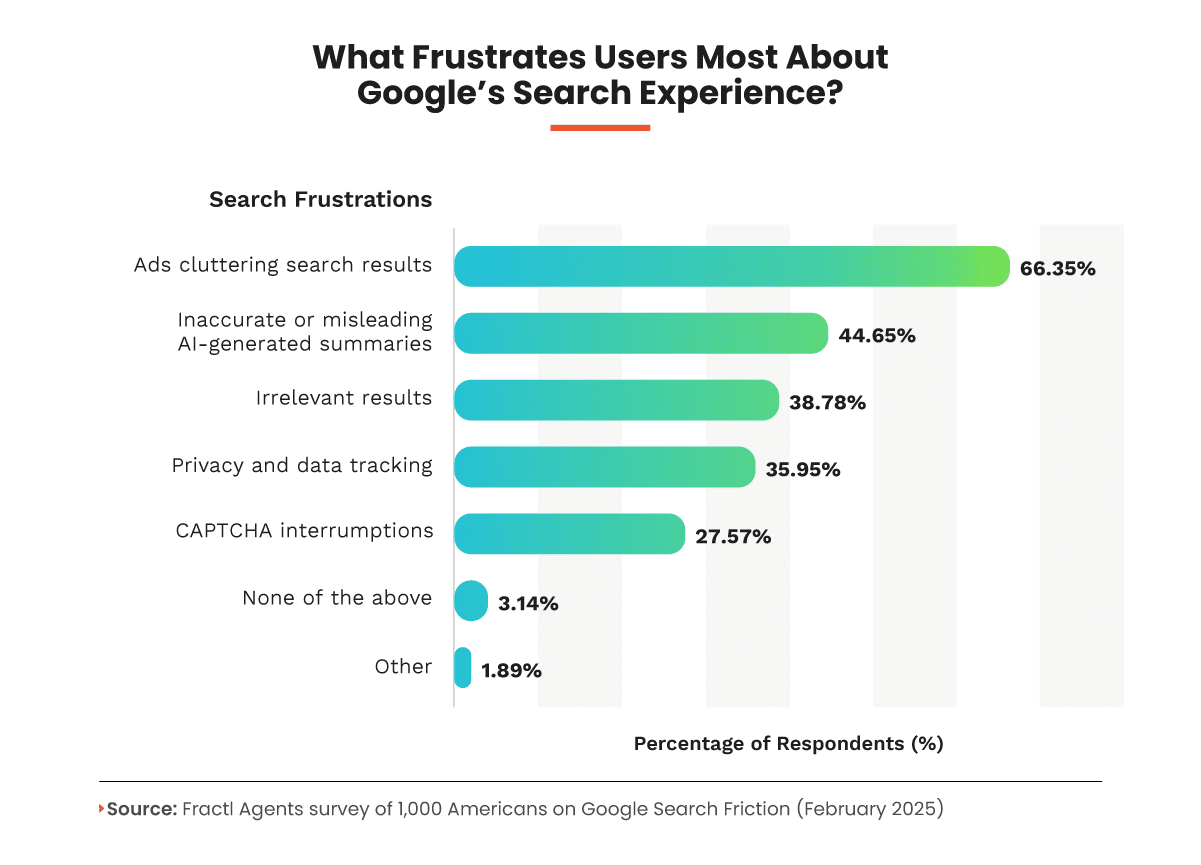
What I found was that the average consumer felt many of the same frustrations I felt every day as a search marketer:
- Google’s search experience frustrates users primarily due to excessive ads cluttering results (66.4%), making it harder to find valuable, organic content.
- Many also dislike inaccurate or misleading AI-generated summaries (44.7%), which can lead to misinformation.
- Irrelevant search results (38.8%) further add to the dissatisfaction, reducing efficiency.
- Privacy concerns, such as data tracking (35.9%) and frequent CAPTCHA interruptions (27.6%), also contribute to a less-than-ideal user experience, disrupting seamless browsing.
The open-ended responses were the most entertaining (and something I plan to expand upon during my SMX Advanced session this summer in Boston).
Dig deeper. Survey: 54% of people look through more search results vs. 5 years ago
For today’s entertainment value – it’s not just our industry that has been sharing these frustrations over Google’s volatile SERPs, as the open-ended responses alluded to many of the same concerns we’ve all lamented over:
- Content quality issues
- “Lately all the search results are always from Reddit.”
- “Lack of relevant results in general – often, I will search for something and it will give me results for the opposite of what I searched for.”
- “Filtering certain links.”
- “It will provide out-of-date information.”
- “Multiple results with the same information.”
- AI-related frustrations
- “Please remove the AI-generated answers.”
- “The AI in general – usually I am on Google to go on other webpages.”
- “No toggle to remove AI search, search parameters seem to get ignored.”
- “Inability to opt out of AI summaries.”
- CAPTCHA complaints
- “Captcha services that refuse to accept answers, particularly the ones that load new images in over five-second delays.”
- “CAPTCHAs that are largely nonsensical/hard to understand what is wanted from the user.”
- Monetization and bias concerns
- “That search results are influenced by money paid to Google.”
- “Pushing Google apps, like always trying to open Google Maps.”
- “Sponsored websites.”
- “The censorship of conservative viewpoints and people.”
While I’m not alone in my CAPTCHA frustrations, many users (36.8%) rarely encounter CAPTCHAs (1-2 times per week), while 32.5% never experience them.
However, 22.1% reported occasional disruptions (3-5 times per week), and a smaller group (6.8%) faced them frequently (6+ times per week), with 1.8% dealing with daily interruptions. (Hello, fellow digital marketers!)
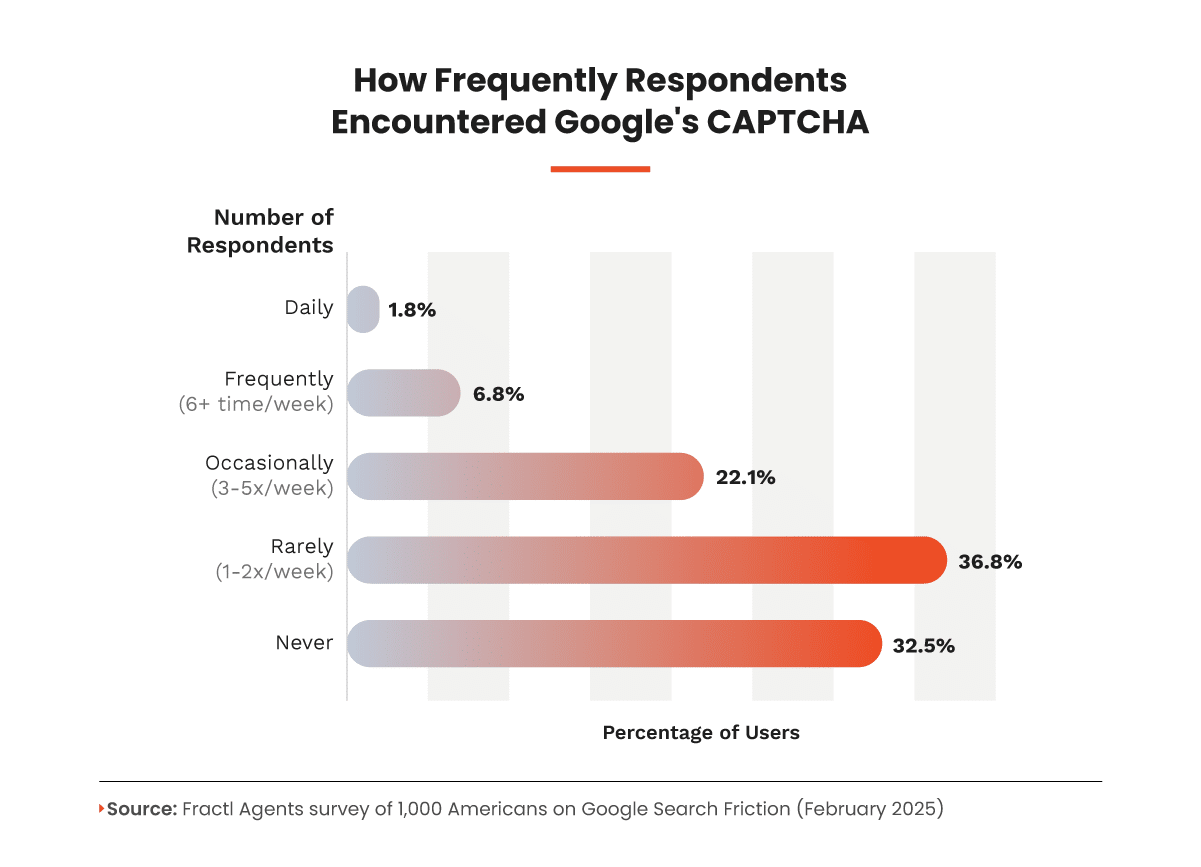
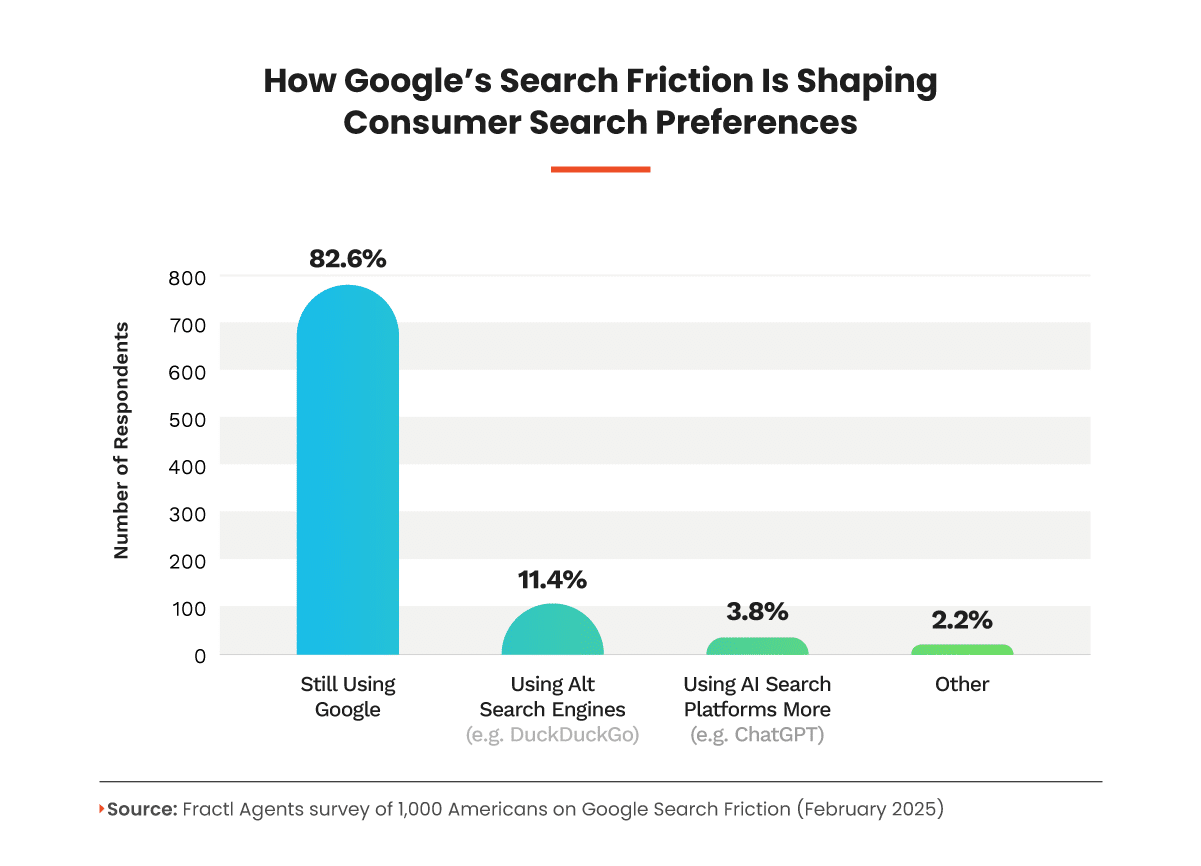
But here’s the kicker: despite these interruptions, Google still holds its ground as the dominant search engine for 82.6% of respondents.
That said, friction does lead to shifts.
Around 11.4% of users are exploring privacy-first alternatives like DuckDuckGo and Brave, while 3.8% are venturing into AI-powered search tools like ChatGPT and Claude.
This signals an emerging shift in consumer behavior driven by usability pain points that other search products are solving for.
With increasing search quality concerns nudging users toward different search experiences, it’s only a matter of time before these small behavioral shifts compound into more significant market trends.
Google still dominates consumer search – and likely will for the next few years.
However, the rise of alternative search engines, AI-driven discovery tools, and direct interactions with LLMs means diversification should be on your radar if you work in marketing.
How to drive brand visibility with generative engine optimization: Myths vs. facts
Generative AI is changing how people search, but brands are still approaching it with an outdated SEO playbook.
It’s time to debunk the biggest misconceptions about GEO and outline what actually works to increase brand visibility in AI-generated responses.
To deepen our understanding of the current industry beliefs around AI rankings, my co-founder, Kristin Tynski, and I analyzed the past six months of mentions of “ChatGPT+Rankings” and “AI+Rankings” on LinkedIn.
We found 403 unique LinkedIn posts that provided a view of how AI is discussed in professional circles, which we further analyzed through multi-label classification, sentiment analysis, temporal trend mapping, and advanced topic modeling.
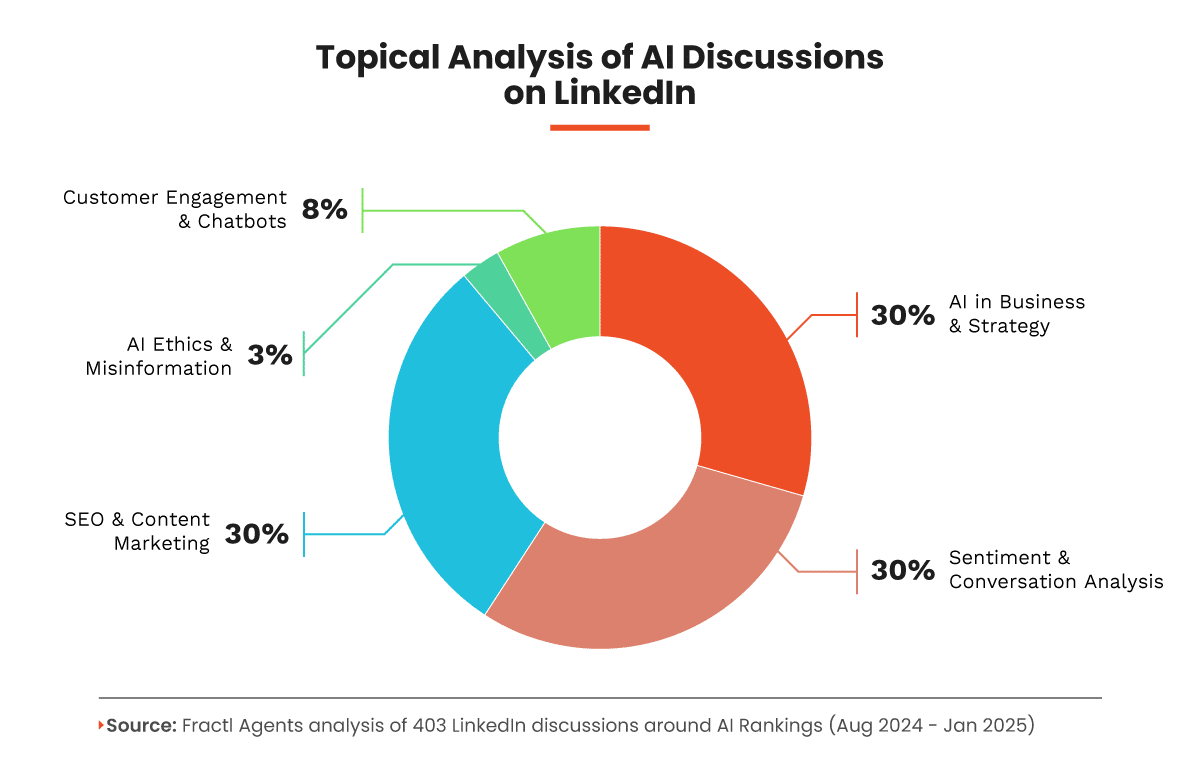
By leveraging a Latent Dirichlet allocation analysis for topic modeling, we were able to quickly distill the topics of interest for those who are on the bleeding edge of AI in marketing.
Majority of conversations focusing on four key themes:
- AI in business strategy: Focus on workflow automation, decision support, and predictive analytics.
- Digital marketing and SEO: Emphasis on content automation, ranking strategies, and data-driven marketing.
- Customer engagement and chatbots: Exploration of AI’s role in customer service and the balance between automation and human interaction.
- AI ethics and misinformation: Discussion of bias, transparency, and responsible AI deployment.
Most LinkedIn posts spanned multiple topic clusters, reinforcing that professionals view AI as an integrated force influencing various business functions.
Frequent keyword pairings included:
- “AI and automation.”
- “Content optimization and predictive analytics.”
- “Chatbot and customer engagement.”
This indicates a view of AI as a comprehensive tool for operational and strategic improvement.
Compared to past data, current discussions showed a trend toward more positive sentiment and a heightened focus on ethical considerations.
Above all else, the highest-engagement posts commonly articulated the view that “AI is a partner, not a replacement,” emphasizing the need for human oversight.
After years of testing AI workflows and developing proprietary tools, we’ve seen firsthand how AI’s efficiency, combined with human strategy, drives brand growth and maximizes marketing ROI.
Yet, many brand leaders still don’t understand how AI engines work.
Skepticism is rising as everyone scrambles to establish thought leadership in a space they barely grasp.
In an industry long plagued by snake oil salesmen, separating fact from fiction has never been more critical for marketers who want to stay on the bleeding edge of innovation and the future of search.
Myth 1: AI search works like Google’s live web indexing
Reality: LLMs primarily rely on pre-trained datasets, but some models can retrieve real-time information through internet-connected sources and RAG.
Understanding the difference in AI models is key to understanding how to potentially influence your brand’s visibility in these up-and-coming answer engines.
Seer Interactive put together a helpful chart to help drive this industry education:
Simply put, while Google’s search index is continuously refreshed, most LLMs rely on historical snapshots of the web and are not updated in real time.
Unless explicitly retrained, they may miss new articles, trends, or emerging discussions.
While Tynski believes this will change before the end of the year, frequent retraining remains prohibitively expensive, meaning most models still operate on static data that can be months – or even years – old:
- GPT 4o: Last training update was December 2023.
- Claude 3.5 Sonnet: Trained on data up until April 2024.
As a result, real-time events and newly published content may not always appear in AI-generated responses unless the model has direct access to live data sources.
Key takeaways for adapting your brand strategy for LLM visibility
- In cases where AI-driven search platforms leverage real-time search integrations (e.g., ChatGPT’s “Search the web”), it’s valuable for brands to leverage proactive and reactive PR strategies to maintain frequent and fresh mentions that will be integrated into real-time data queries against authoritative news sources.
- Because LLMs don’t have fixed rankings and AI responses vary based on query phrasing, context, and model updates, businesses should use tracking tools to monitor their brand visibility across major AI models for a wide range of relevant queries.
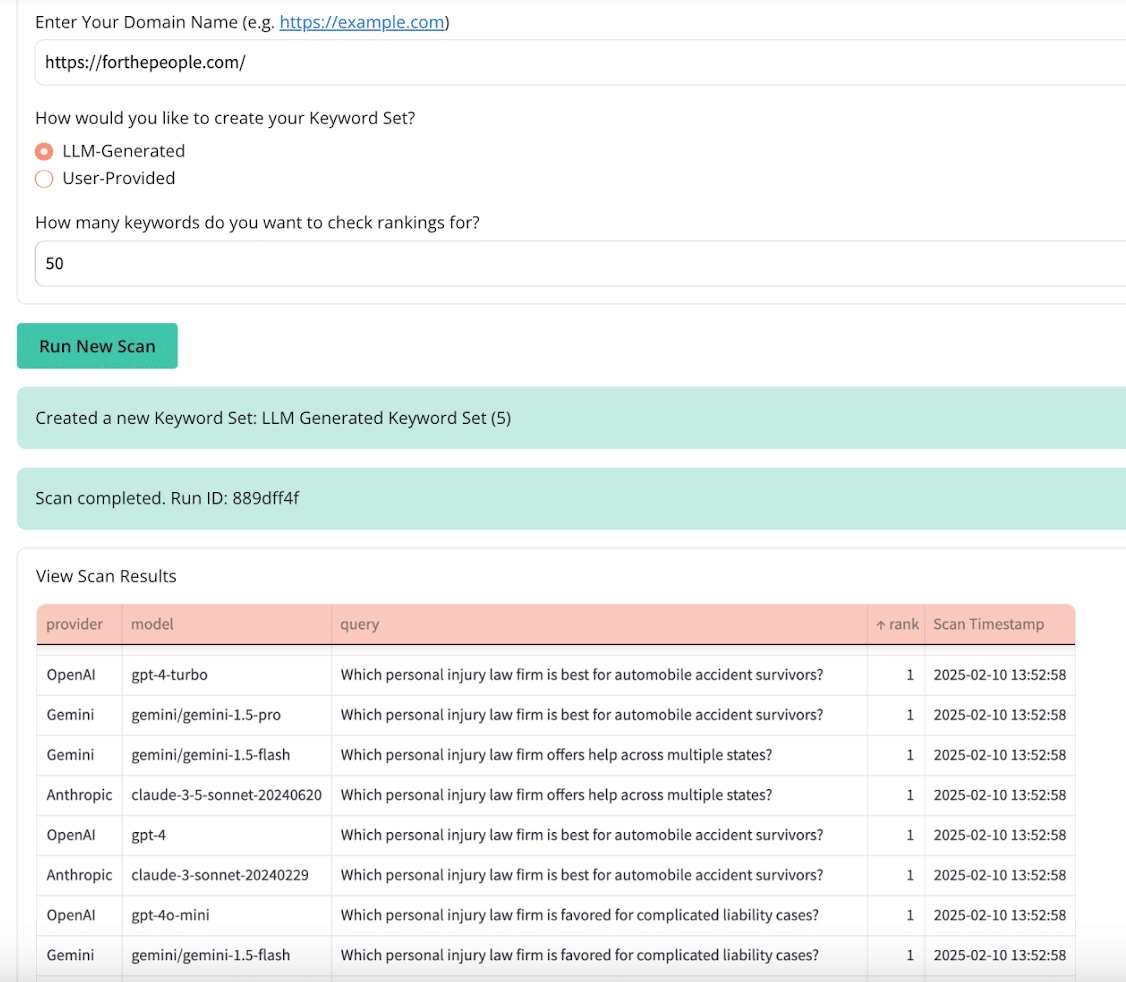
Dig deeper: Decoding LLMs: How to be visible in generative AI search results
Myth 2: Links are the key to ranking in AI responses
Reality: LLMs prioritize brand mentions, contextual relevance, and entity associations.
For decades, SEO revolved around link building.
Earning backlinks from high-authority sites was the golden ticket to building domain authority, trust signals, and rankings.
But LLMs don’t “rank” content the same way Google does.
They don’t crawl and index live web pages. They generate responses based on pre-trained data, considering word frequency, contextual relevance, and surrounding content.
However, context matters as much as the mention itself.
LLMs aggregate references from multiple sources and generate responses non-deterministically.
As such, the visibility of a brand or idea depends on how often and in what context it appears across reputable training data.
Some AI-powered search engines, like Perplexity, use retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) – pulling from live search results to refine AI-generated responses.
While this means traditional rankings still influence LLM-driven search, being part of a trusted corpus matters more than individual rankings.
Ultimately, appearing in trusted, widely referenced sources – especially those with a strong likelihood of being part of an LLM’s training data – significantly increases your brand’s chances of being mentioned in AI-generated answers.
This should be a big win for digital PR teams who constantly tout the benefits of a text mention for clients who become enraged when a journalist covers their brand name without providing a link.
Tips for maximizing brand visibility in AI search with mentions and context
- Build your brand’s topical authority across entities by developing brand thought leaders and expert commentary to position your brand as a valuable source within high-context discussions across publishers and Q&A forums.
- Develop industry analyses and research-backed content that build brand authority and increase credible mentions, ensuring AI models reference and retrieve your content in responses.
- Leverage digital PR to secure brand mentions in high-authority publications, increasing your brand’s share of voice in LLM training data, including the diverse and credible publications outlined above.
Dig deeper: How to monitor brand visibility across AI search channels
Myth 3: It’s impossible to know which sources LLMs use for training data
Reality: Research and monitoring tools can inform likely training sources and brand visibility.
Although AI companies don’t disclose their full training datasets, there are ways to research and approximate where LLMs pull data from.
For example, you can query ChatGPT for a list of publishers OpenAI has partnered with for its training data.
While this response won’t be immediately exhaustive, it can provide clues about high-priority domains your digital PR team might want to prioritize for brand mentions depending on your vertical and brand expertise:
- Associated Press (AP): In July 2023, OpenAI and AP signed a deal allowing the AI company to license AP’s content archive going back to 1985 for training purposes.
- News Corp: In May 2024, OpenAI entered into an agreement with News Corp to integrate news content from The Wall Street Journal, New York Post, The Times, and The Sunday Times into its AI platform.
- The Atlantic and Vox Media: In May 2024, OpenAI signed deals with The Atlantic and Vox Media to share content, aiming to enhance the accuracy of AI models like ChatGPT by incorporating reliable news sources.
- Condé Nast: In August 2024, Condé Nast, publisher of titles such as The New Yorker, Vogue, and Vanity Fair, entered a multi-year deal with OpenAI, allowing the AI company to use content from its properties in ChatGPT and other products.
- Axel Springer: In December 2023, Axel Springer, owner of publications like Politico and Business Insider, partnered with OpenAI to have its content summarized within ChatGPT, including paywalled articles, with links and attribution.
- Future: In December 2024, OpenAI partnered with Future, bringing content from over 200 media brands, including Marie Claire, PC Gamer, and TechRadar, to ChatGPT.
- Hearst: In October 2024, OpenAI announced a partnership with Hearst, integrating content from its magazines and newspapers, such as the Houston Chronicle, San Francisco Chronicle, ELLE, and Runner’s World, into ChatGPT.
- GEDI: In September 2024, OpenAI partnered with GEDI, an Italian media group, to provide ChatGPT users access to high-quality Italian-language journalism.
- TIME: In June 2024, OpenAI entered a multi-year partnership with TIME, granting access to 101 years of archival content to enhance its products and display in response to user inquiries.
- Le Monde and Prisa Media: In March 2024, OpenAI signed contracts with Le Monde and Prisa Media to bring French and Spanish news content to its AI models.
- Reddit: In May 2024, Reddit and OpenAI announced a partnership to integrate Reddit’s content into OpenAI products, including ChatGPT, providing real-time, structured content to enhance AI tools.
- Axios: In January 2025, OpenAI announced a content partnership with Axios, expanding its work with the news industry.
Beyond querying LLMs directly, there are tools that analyze which publishers and articles influence LLM training.
Understanding how your brand appears in these datasets is crucial, as it affects AI-generated content, search visibility, and overall brand perception.
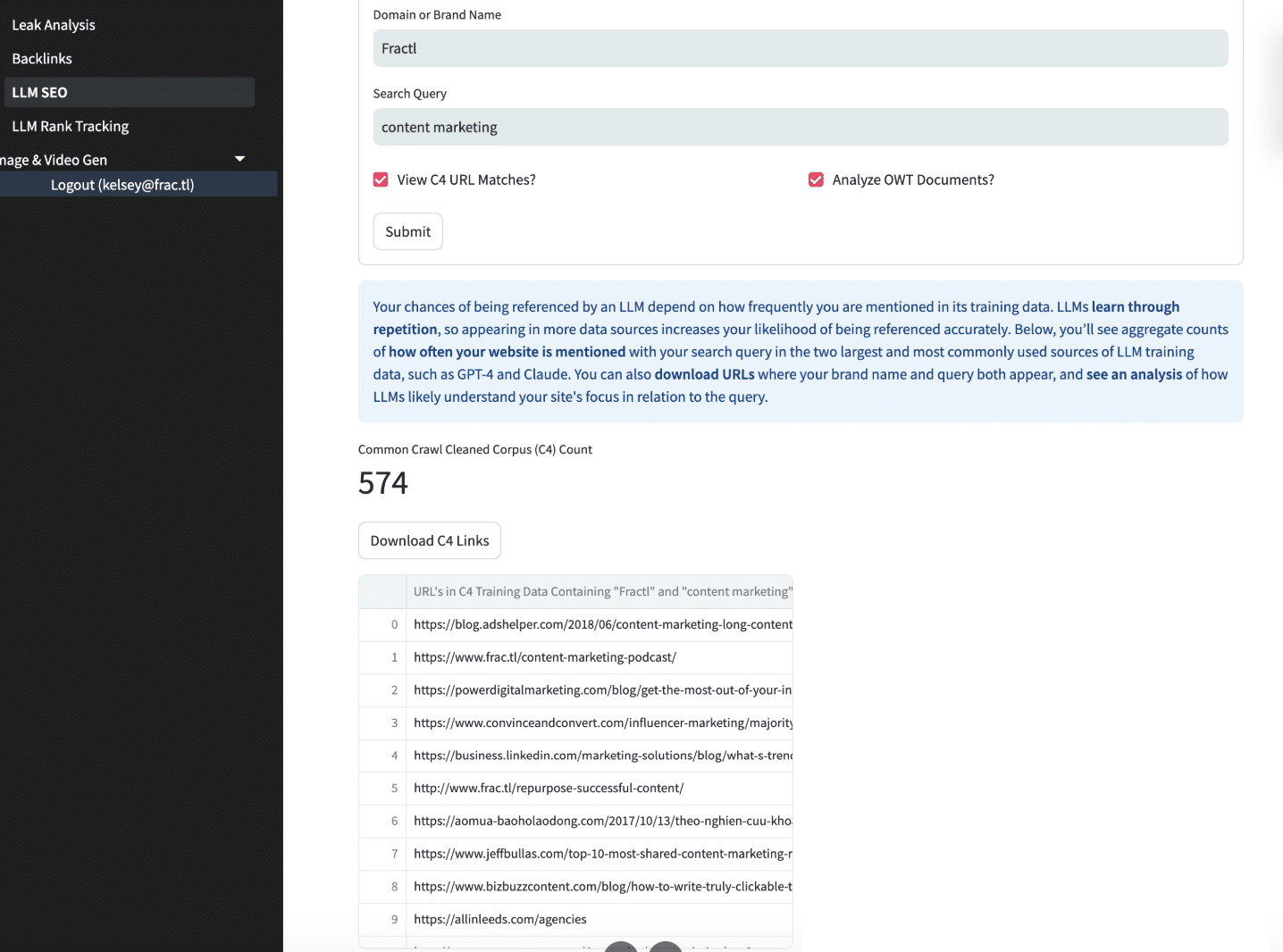
Ways to track sources for LLM training data
- Use tools to monitor how your brand appears in Common Crawl data to understand how your content and brand mentions influence LLM training, AI-generated responses, and brand visibility.
- Use platforms like SparkToro and BuzzSumo to help identify which sites influence your audience and likely have a high influence in your industry from which AI models may be drawing data.
Pioneering strategies in the age of agentic workflows
In 2025, SEO is about building the kind of brand trust and semantic authority that LLM-based ranking systems value, in the same way we have always suspected of Google.
If you’re driving AI adoption within your organization, understanding the pitfalls of AI and developing trends in this emerging search frontier will help ensure your career for years to come.
- Position AI as an enhancement, not a replacement: AI should augment workflows, streamline processes, and improve decision-making – but human expertise remains essential for trust and strategic oversight.
- Proactively address AI ethics and misinformation: Brands should establish clear AI ethics guidelines, ensure transparency in AI-generated content, and prioritize credibility to build long-term audience trust.
- Leverage AI chatbots with human oversight: AI-powered engagement tools enhance customer interactions but require monitoring and fine-tuning to maintain accuracy and user experience.
- Drive brand credibility and visibility in LLMs: Consistently publishing high-quality content and securing brand mentions in trusted sources strengthens your brand’s entity recognition, contextual relevance, and authority – ultimately increasing visibility in AI-generated responses.
- Track your brand’s presence in AI models: Use monitoring tools to analyze how AI platforms reference your brand in key search queries. Optimize your content strategy by assessing your visibility against competitors for common FAQs relevant to your target audience.
Companies that embrace this evolving search landscape will be the ones dominating brand visibility in the future of AI-driven search over the next 12-36 months.
Brands that hesitate may find themselves losing valuable traffic to competitors who were early adopters in the age of AI.
source https://searchengineland.com/optimize-content-strategy-ai-powered-serps-llms-451776



0 Comments